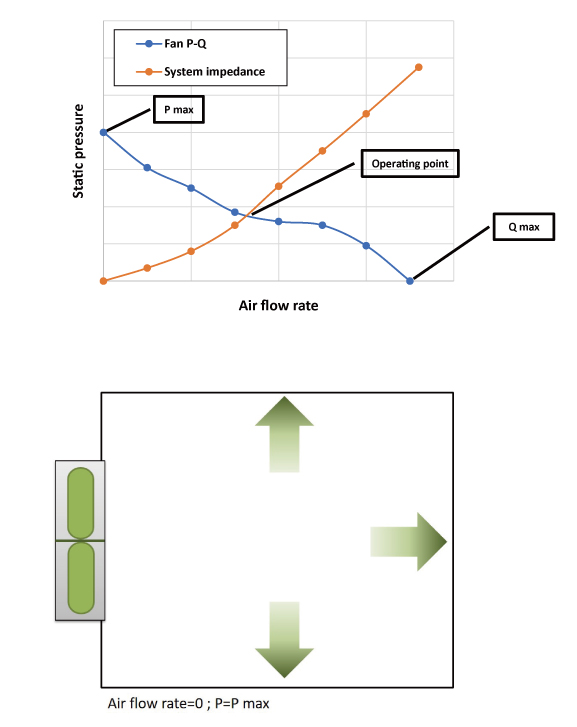
Each fan gets a characteristic curve, also known as P-Q curve, which indicates the correlation between fan air flow rate and static pressure.
Fan’s air flow rate is total amount of air passing through fan itself per unit of time, the three most common measures for the air flow used are Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM), cubic Meters per hour (m3 / hr), and liters per minute (l / min).
The maximum air flow rate at one end of the curve refers to the maximum air flow rate that the fan can provide in a total free and open space without any impedance.
The static pressure is the resistance that fan can overcome; the maximum static pressure refers to the measured wind pressure in the fully enclosed channel.
While the fan is installed in different systems or products, actual airflow blowing through may vary due to flow impedance from the system, which is known as “fan’s operating point”. The air flow rate at the operating point is the amount of air actually passing through, which can be calculated by CFD simulation or by experiment with wind tunnel equipment.

 繁體中文
繁體中文  English
English