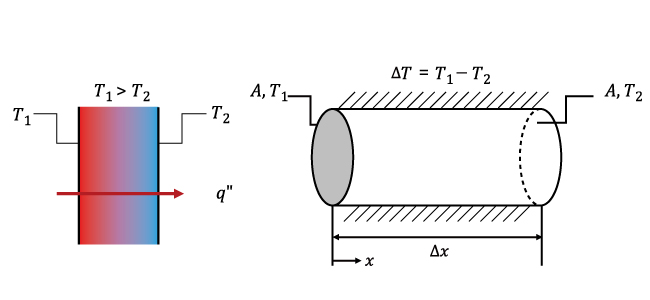
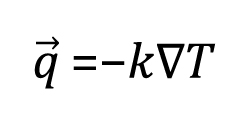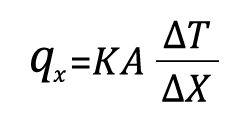When a temperature gradient exists in a stationary medium, the heat transits from higher temperature to the other end via molecular activity.
The rate equation for heat conduction is also known as Fourier’s law.
Assuming a uniform medium, and temperature at both ends is constant, the one-dimensional heat transfer is listed as:

 繁體中文
繁體中文  English
English